Office 2013 include applications such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook. They’re available as a one-time purchase for use on a single PC. Microsoft 365 plans include premium versions of these applications plus other services that are enabled over the Internet, including online storage with OneDrive and Skype minutes for home use. Office 2013 include applications such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook. They’re available as a one-time purchase for use on a single PC. Microsoft 365 plans include premium versions of these applications plus other services that are enabled over the Internet, including online storage with OneDrive and Skype minutes for home use. Microsoft Excel 2013 is a program that allows you to discover and reveal the insights hidden in your documents data. Update for Microsoft Excel 2013 (KB2760339). Excel uses the standard math rules of operator order in formulas. I find the following mnemonic helpful in remembering these: 'Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally'. Parentheses first, innermost if nested.
APPLIES TO: 2013 2016 2019 SharePoint in Microsoft 365
Excel Services in SharePoint Server 2013 enables you to share all or parts of an Excel workbook with other people in a central location. When you publish a workbook to SharePoint Server 2013, you can choose between several browser view options (such as worksheet view and gallery view). You can also choose to display Excel content in a special SharePoint Web Part known as the Excel Web Access Web Part. To learn how to share workbooks using Excel Services, see this article.
In this article
Before you begin
Before you begin this task, review the following info about prerequisites:
You must be using Excel and SharePoint Server 2013.
Excel Services must be configured to include a trusted data connections library and a trusted document library. Ideally, you'll have a Business Intelligence Center site configured that you can use for your data connections and workbooks. For more info, see Configure a Business Intelligence Center in SharePoint Server 2013.
You will need info from a SharePoint admin about how data authentication is configured for the databases your organization uses. This can affect how you connect to different data sources.
You must have at least Contribute permissions assigned to you for the SharePoint library where you plan to publish the workbook.
You should have already created an Excel workbook that contains at least one item, such as a chart, table, PivotChart report, PivotTable report, or range of data.
If you plan to publish workbooks that contain data models to SharePoint Server 2013, Excel Services must be configured to support data models. For more info, see Configure Excel Services in SharePoint Server 2013 Preview.
If you plan to publish a workbook that contains a Power View sheet, SQL Server Reporting Services must be configured in SharePoint integrated mode. For more info, see Install SQL Server BI Features with SharePoint 2013 (SQL Server 2012 SP1).
Share workbooks using Excel Services
Suppose that you have created an Excel workbook that contains info that you want to share with others. Suppose additionally that you might want to display some content in that workbook in multiple locations. Excel Services enables you to do this by following a simple process:
Define one or more named items in the workbook. These items can be charts, tables, PivotChart reports, PivotTable reports, ranges of data, and so on.
Choose browser view options for the workbook. You can choose between worksheet view or gallery view.
Publish the workbook to a SharePoint library. Ideally, you'll use a library such as a Document library in a Business Intelligence Center site.
(This is optional.) Display all or part of an Excel workbook in an Excel Web Access Web Part.
The following sections describe how to perform the steps to share a workbook by using Excel Services.
Define named items in a workbook
Defining named items is not an absolute requirement for sharing a workbook by using Excel Services. However, as a best practice, we recommend that you define named items in Excel. Doing this can avoid confusion later, especially if you want to display a single item in a SharePoint Web Part (instead of displaying the whole workbook in the Web Part). A named item can be a chart, table, a PivotChart report, a PivotTable report, a slicer, a Timeline control, a worksheet, or even a range of data in a worksheet.
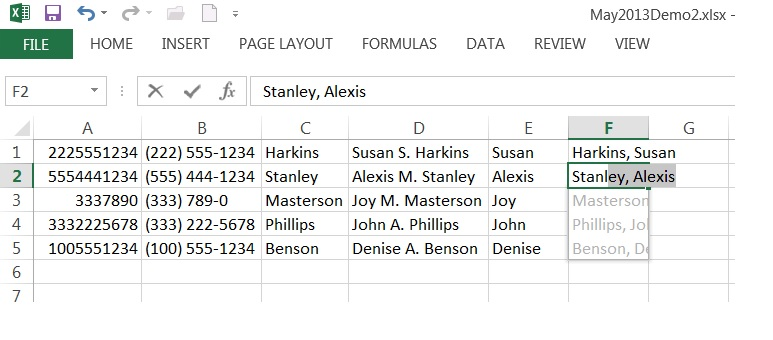
As you create items, such as PivotChart reports, PivotTable reports, slicers, Timeline controls, and so on, each item is given a name by default in Excel. For example, suppose that you create a PivotTable report on Sheet1 in Excel. By default, that PivotTable report will be labeled as PivotTable1. Now suppose that you add a PivotChart report to that same worksheet. Its default name will be PivotChart1. If you open Sheet2 and create a PivotTable report on that worksheet, its default name will be PivotTable1. It's easy to become confused between PivotTable1 on Sheet1 and PivotTable1 on Sheet2. Defining each of these items as named items using unique names can avoid this confusion. Use the following procedure to define named items in Excel.
To define named items in a workbook
In an Excel workbook, identify a worksheet, chart, table, range of data, or other element that you want to define as a named item. Select the range of cells that contains the item (or items) that you want to include in the named item.
To define the whole worksheet as a named item, choose an empty cell in the worksheet, and then press CTRL+A.
On the Formulas tab, in the Defined Names group, choose Define Name to open the New Name dialog.
In the Name box, type a name for the item. Choose a unique name that won't be repeated in the workbook.
In the Scope list, choose Workbook.
Use the Refers to box to confirm or edit the range of selected cells.
Click OK.
Repeat steps 1-6 for each item that you want to define as a named item.
Specify how you want a workbook to be displayed
When you use Excel Services to share a workbook, you can choose how you want the workbook to be displayed in a browser window. Specifically, you can choose from the following browser view options:
Worksheet view. This option causes a whole worksheet to be displayed in a browser window, such as it is displayed in Excel.
The following image shows an example dashboard rendered in worksheet view.
Gallery view. This option causes one item, such as a PivotChart report or a PivotTable report, to be displayed prominently in the center part of the browser window. Slicers, filters, and Timeline controls are displayed along the left-hand side of the browser window. Additional items, such as other PivotChart reports or PivotTable reports, are displayed as thumbnail images along the right-hand side of the browser window. In gallery view, people can choose a thumbnail image to change which item is featured in the center part of the browser window.
The following image shows the same example dashboard rendered in gallery view.
Use one of the following procedures to specify browser view options for the workbook.
To configure the workbook to display using worksheet view
In Excel, on the File tab, click Browser View Options.
On the Show tab, use the list to select Sheets, select the worksheets that you want to display, and then click OK
Save the workbook, and then close Excel.
To configure the workbook to display using gallery view
In Excel, on the File tab, click Browser View Options.
On the Show tab, use the list to select Items in the Workbook.
Select the named items that you want to display, and then click the Parameters tab.
If the workbook contains slicers or a Timeline control, click Add, select slicers or Timeline controls that you want to display, and then click OK.
Click OK to close the Browser View Options dialog.
Then close Excel.
After you have specified browser view options for a workbook, the next step is to publish the workbook to SharePoint Server 2013.
Publish a workbook
When you publish a workbook you add it to a SharePoint library, such as a Document library in a Business Intelligence Center site. The location that you use must be specified as a trusted location for Excel Services.
To publish a workbook to a SharePoint library
Open a web browser.
In the address line, type the address to a library in SharePoint Server 2013. For example, you might use a SharePoint address that resembles http://servername/sites/bicenter/documents or http://servername/SharePointsitename/documentlibraryname.
Note
To specify a location as a trusted location in Excel Services, see Manage Excel Services trusted file locations (SharePoint Server 2013).
In the library that you selected, choose + New Document to open the Add a Document dialog.
Choose Browse, and then use the Choose File to Upload dialog to select the workbook that you want to publish. Then choose Open.
In the Add a document dialog, choose OK. The workbook is added to the library.
Now that you have published a workbook to a SharePoint library, you can display content from that workbook in an Excel Web Access Web Part.
Display Excel content in an Excel Web Access Web Part

Excel Services in SharePoint Server 2013 includes a special SharePoint Web Part called the Excel Web Access Web Part. This Web Part enables you to share all or part of an Excel workbook in its own Web Part on a SharePoint Web Part page. You can display a single item that is defined as a named item, or you can display the whole workbook in that Web Part.
The following procedures describe how to add an Excel Web Access Web Part to a SharePoint page and then display content in the Web Part.
To add an Excel Web Access Web Part to a SharePoint site
Begin with a SharePoint page open for editing.
In a zone on the page, choose the hypertext that says Add a Web Part.
Panes showing available categories and kinds of Web Parts appear near the top of the page.
In the Categories pane, choose Business Data. Then, in the Parts pane, choose Excel Web Access.
Choose Add to add the Web Part to the page. Keep the page open for editing.
The next step is to connect a workbook to an Excel Web Access Web Part.
To display Excel content in an Excel Web Access Web Part
Begin with a SharePoint page open for editing and an empty Excel Web Access Web Part added to the page.
In the empty Excel Web Access Web Part, in the Select a Workbook section, click the hypertext that says Click here to open the tool pane. The tool pane opens.
In the Workbook Display section in the Workbook text box, specify the web site address (URL) for the workbook. If you do not know the URL, click the Browse button, navigate to the library where the workbook was published, select the workbook that you want to use, and then click Insert.
(This is optional.) To display a single item, such as a chart, table, PivotChart report, or PivotTable report, in the Named Item box, type the name of the item. This causes only that item to be displayed in the Web Part, instead of displaying the whole workbook.
At the bottom of the tool pane, click OK.
The workbook is now displayed in the Web Part. If you want, you can proceed to specify navigation and interactivity settings for the Excel Web Access Web Part.
To specify navigation and interactivity settings for a workbook displayed in an Excel Web Access Web Part
Begin with a SharePoint page open for editing. In the upper-right corner of the Excel Web Part, choose the down arrow to open the Web Part menu, and then choose Edit Web Part. The Excel Web Part tool pane opens.
In the Toolbar and Title Bar section and in the Navigation and Interactivity section, select the properties that you want to enable. If you want to disable a property, clear its check box.
At the bottom of the tool pane, choose OK to apply your changes and close the tool pane.
In the SharePoint site, click Stop Editing to save your changes.
See also
Concepts
77-427: Microsoft Excel 2013 Expert Part One
Languages: en zh-cn zh-tw de es fr it ja ko nl pt-br ru ar-sa
Retirement date:
Expert-level candidates for the Excel 2013 exam should have an advanced understanding of the Excel environment and the ability to guide others in the proper use of features in Excel 2013 of Office Professional Plus.
Price based on the country in which the exam is proctored.
2013 Excel Formulas And Functions
for Microsoft Excel 2013 Expert Part One2013 Excel Winslow
All objectives of the exam are covered in depth so you'll be ready for any question on the exam.


Comments are closed.