Atom as a whole is electrically neutral so that the number of protons and the number of electrons must be the same. But there is no rule for that the number of proton must be equal to number of neutrons. Sometimes, the number of proton is unfortunately equal to the number of neutrons. But it is very very rare.
- The number of protons and electrons in an atom or molecule determines its charge and whether it is a neutral species or an ion. This worked chemistry problem demonstrates how to determine the number of protons and electrons in an ion.
- How many electrons protons and neutrons are there in an atom of 30si? As it turns out, silicon has five main isotopes - each with a unique number of neutrons. Silicon has 14 protons and assuming the piece of silicon has no overall charge each atom will have 14 electrons.
What is Atomic number?
Atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It can also be the number of electrons in a neutral atom. Pay attention to the word neutral. The proton number is so important that it is used to identify an element. As a result, all the elements on the periodic table (an organized table of elements) are arranged based on increasing atomic number. So as you move from left to right on the periodic table the atomic number of the elements increase step-by-step.
What’s Neutron number?
Neutron number is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
What’s Mass number?
Mass number is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. As you can tell, the number of electrons are not included in the mass number, which means that the mass number is not the same thing as the mass of the atom (atomic mass). If you know the mass number and atomic number, you can always find the number of neutrons by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number.
What symbols are used to describe an atom?
The chemical symbol of the element is represented by the letter E. The mass number (superscript, A) and the atomic number (subscript, Z) appear on the left hand side of the chemical symbol. These symbols vary from element to element. Now, let’s apply these concepts to complete the following table
From the table, you are given the atomic and mass number of Mg and the mass number of Kr. To complete the first row on the table, you have to remember that the proton number is the subscript on the left side of the chemical symbol and is the same as the atomic number. And since the atom is neutral, the number of electrons and protons are equal. For Kr, you have to look for its atomic number from the Periodic Table.

From the periodic table, the atomic number of Kr is 36. Therefore to get the number of neutrons, you must subtract the atomic number (36) from the mass number ( 84). The last two rows have no chemical symbols, therefore, you must use their atomic numbers to identify the elements on the periodic table. To get the atomic number for the last row, you must remember that since the atom is neutral, the number of electrons are the same as the number protons.
How do you know an atom is neutral?

Sometimes you can deduce by checking whether the number of electrons are the same as the number of protons. In our example you don’t have to do that because I already wrote under the table that all the elements are neutral. Thus, the number of protons is 6. To get the mass number, you must add the number of protons to the number of neutrons. Here is the completed table:
What’re isotopes?
From the table, you can see that both carbon atoms have an atomic number of 6 but a mass number of 6 and 7. Why is that? Is so because in nature you can have an element that consists of atoms with the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons. When this happens, we usually call the different versions of the same element isotopes. So if we call them by their mass numbers, we will say carbon-12 (read as carbon twelve) and carbon-13 are isotopes of carbon, and they have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
To learn how atoms form ions, click here.
Protons, electrons and neutrons are the major constituents of an atom. There are thousands of varieties of atoms and each has different sets of those above-mentioned particles, the number of constituents is what defines them.
Find Number of Protons, Electrons and Neutrons
Number of Protons
Protons are positive charge carriers, each has positive 1.6*10^-19 coulomb charge and mass 1.673*10^-24 grams. The number of protons in an atom also called atomic number is different for different elements, the same element has the same number of protons in their atoms.
It is represented by Z. Whenever someone says carbon, you can precisely say that it has 6 protons, this is why it is called carbon. Or, an element with 6 protons in their atoms is called carbon.
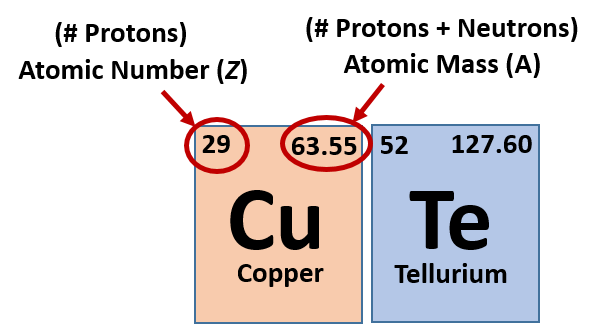
Same follows for hydrogen or oxygen or nickel or copper with 1 or 8 or 28 or 29 protons respectively. They have a number of protons which defines what element are they. Also, it defines the chemical and physical properties of an atom.
Number of Electrons
Electrons are negative charge carriers, each has negative 1.6*10^-19 coulomb charge and mass 9.1*10^-28 grams. The number of electrons for an atom in an isolated state is equal to the number of protons because an atom is electrically neutral, the number of positive charges is equal to a number of negative charges. However, for ions, the number of electrons may be different.
Number of Neutrons
Neutrons have no charge but mass nearly as equal to of proton i.e. 1.675*10^-24 grams. The number of neutrons in an atom is not fixed, same elements may have atoms with different number of neutrons. Number of neutrons in an atom is obtained by subtracting atomic number from atomic mass (Z) i.e A – Z.
How To Find The Number Of Protons
Hydrogen has one proton but can have 0 or 1 or 2 neutrons. But, almost 99.98% of the hydrogen atoms found in nature have zero neutrons. Similarly, there are variations in number of neutrons for each and every element resulting different isotopes. These isotopes are found in different proportion in nature according to their stability.

Comments are closed.